Table Of Content

Minority leaders may engage in numerous activities to publicize their party's priorities and to criticize the opposition's. The minority leader has a number of formal and informal party responsibilities. Formally, the rules of each party specify certain roles and responsibilities for their leader.
This California congressional race is currently divided by one vote
Representatives and delegates serve for two-year terms, while a resident commissioner (a kind of delegate) serves for four years. The U.S. Constitution requires that vacancies in the House be filled with a special election. The term of the replacement member expires on the date that the original member's would have expired. Under Article I, Section 2 of the Constitution, seats in the House of Representatives are apportioned among the states by population, as determined by the census conducted every ten years. Each state is entitled to at least one representative, however small its population.
Republican Policy Committee Chairman
Most committee work is performed by twenty standing committees, each of which has jurisdiction over a specific set of issues, such as Agriculture or Foreign Affairs. Each standing committee considers, amends, and reports bills that fall under its jurisdiction. Committees have extensive powers with regard to bills; they may block legislation from reaching the floor of the House.
More From the Los Angeles Times
As there is no legislation at the federal level mandating one particular system for elections to the House, systems are set at the state level. As of 2022, first-past-the-post or plurality voting is adopted in 46 states, ranked-choice or instant-runoff voting in two states (Alaska and Maine), and two-round system in two states (Georgia and Mississippi). Elected representatives serve a two-year term, with no term limit.
Although this process means that only a fraction of proposed legislation actually becomes law, the framers of the Constitution wanted careful deliberation in which diverse views are heard and our rights as citizens are represented and defended. Committees in both houses review bills that have been introduced by their colleagues, holding hearings in which their merits are debated. The two houses of Congress may effectively have the same legislative powers, but they operate differently. Given the shortcomings of the government created by the Articles of Confederation, the framers soon realized that a bicameral legislature at the national level would foster a more representative central government. Indeed, the Articles of Confederation—the first constitution of the United States—established a Congress in which all 13 states (the original 13 colonies) were represented equally in a unicameral (one chamber) legislature, with no Office of the President or executive branch.
Meanwhile, the House’s actions during a rare Saturday session put on display some cracks in what is generally solid support for Israel within Congress. The campaign has said that they have gathered more than 500,000 signatures -- surpassing the necessary threshold, but will continue to gather signatures "until the wheels fall off," a spokesperson told ABC News. The issue is likely to be put directly before voters in November's election. "At the end of the day, your politics is important but it is not worth our souls," he said. "I've known for a while that the votes were there, it just takes a lot of fortitude, a lot of spine," Democratic state Rep. Stephanie Stahl Hamilton, who sponsored the bill, told ABC News' Jaclyn Lee.
One example of a provision repeatedly supported by the House but blocked by the Senate was the Wilmot Proviso, which sought to ban slavery in the land gained during the Mexican–American War. Conflict over slavery and other issues persisted until the Civil War (1861–1865), which began soon after several southern states attempted to secede from the Union. The war culminated in the South's defeat and in the abolition of slavery. All southern senators except Andrew Johnson resigned their seats at the beginning of the war, and therefore the Senate did not hold the balance of power between North and South during the war. Under the Articles of Confederation, the Congress of the Confederation was a unicameral body with equal representation for each state, any of which could veto most actions.
The opposition to the Israel aid represented a minority of Democrats, but reflected the deep resistance to unconditional aid and the divisions in the party on Gaza. Representative Jamie Raskin of Maryland represented a notable new “no” vote among Democrats, and other standouts included Representatives Donald S. Beyer Jr. of Virginia, Earl Blumenauer of Oregon and John Garamendi of California. Because of redistricting, it is not possible to do a one-to-one match for every seat, but some newcomers who align more closely with the far right were elected to seats previously held by Democrats or Republicans who voted to impeach Mr. Trump or to create the Jan. 6 commission. The Constitution empowers the House of Representatives to impeach federal officials for "Treason, Bribery, or other high Crimes and Misdemeanors" and empowers the Senate to try such impeachments. The House may approve "articles of impeachment" by a simple majority vote; however, a two-thirds vote is required for conviction in the Senate. A convicted official is automatically removed from office and may be disqualified from holding future office under the United States.
Representatives of the House are addressed as “The Honorable,” before their names, or as congressman, congresswoman, or representative. The so-called bicameral—from the Latin term for “two chambers”—legislature was created by the framers of the U.S. But it’s important to note that this was not the first format established by the framers for the federal government.
As a result, the process to gain ballot access varies greatly from state to state, and in the case of a third party in the United States may be affected by results of previous years' elections. The late 19th and early 20th centuries also saw a dramatic increase in the power of the speaker of the House. The rise of the speaker's influence began in the 1890s, during the tenure of Republican Thomas Brackett Reed. While the minority leader was the head of the minority party, the majority leader remained subordinate to the speaker.
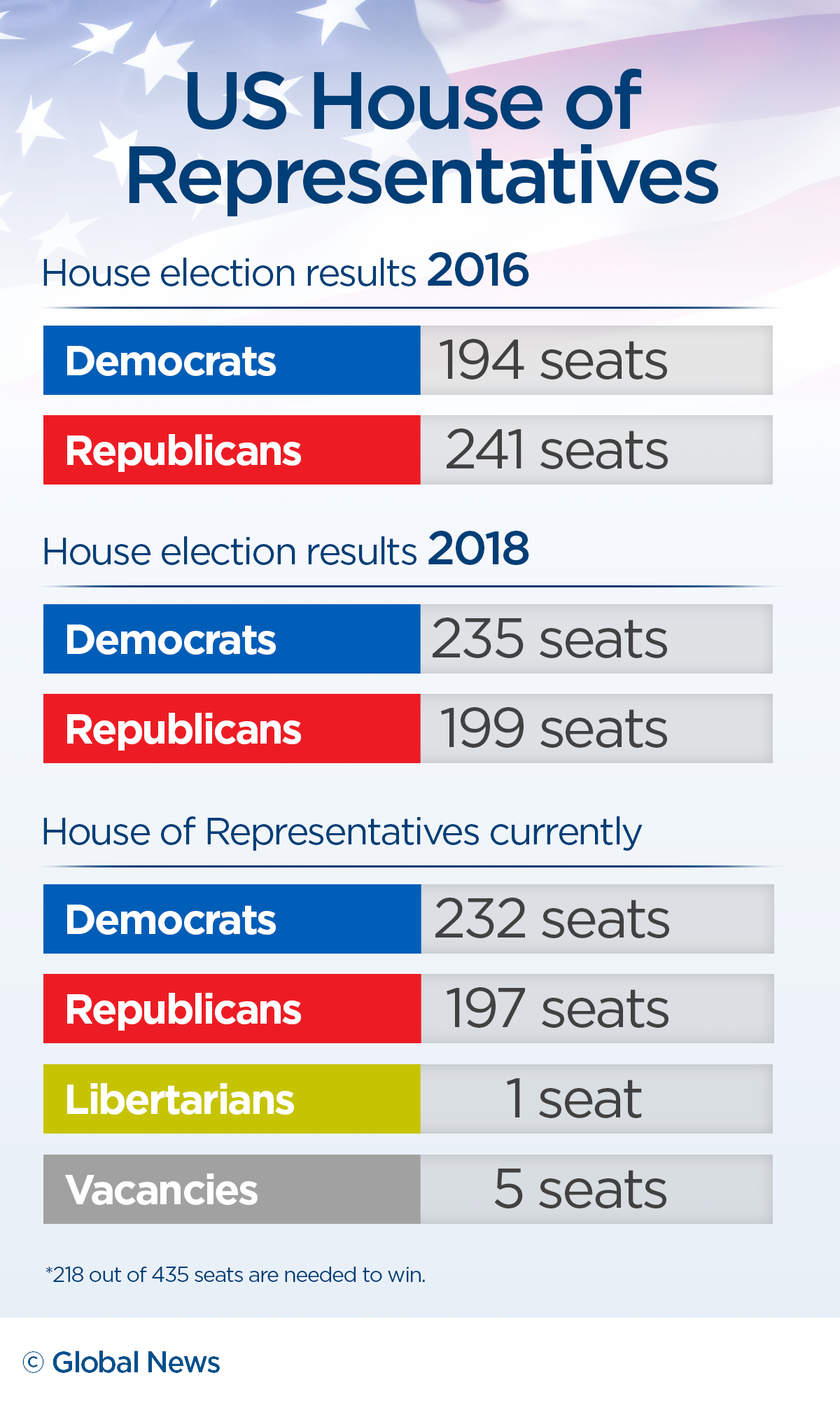
From "How much does the president make?" to "How many amendments are there?" to "What is an oligarchy?" – we're striving to find answers to the most common questions you ask every day. Given the thin Republican majority in the new House of Representatives, Pew Research Center conducted this research to learn about similar situations in the past and how they played out. Slender House majorities (which in this analysis we’re measuring as of the first business day of each Congress) have become more common in the past few decades. After a long run of comfortably large Democratic House majorities from the late 1950s through the early 1990s, narrow majorities – defined for this analysis as margins of control of fewer than 5 percentage points – have prevailed in a third of the 15 most recent Houses. Ballotpedia features 486,932 encyclopedic articles written and curated by our professional staff of editors, writers, and researchers.
After eight years of a more limited confederal government under the Articles, numerous political leaders such as James Madison and Alexander Hamilton initiated the Constitutional Convention in 1787, which received the Confederation Congress's sanction to "amend the Articles of Confederation". Al Jazeera’s Patty Culhane, reporting from Washington, DC, said the number of Republicans who voted against the bill in the House is significantly high. The United States House of Representatives with broad bipartisan support has passed a $95bn legislative package providing security assistance to Ukraine, Israel and Taiwan, despite bitter objections from Republican hardliners. Another Republican state representative, Jacqueline Parker, decried the GOP votes for repeal, calling abortion "akin to slavery."
Narrow majorities are tailor-made for contentious speakership elections, as McCarthy’s weeklong, 15-ballot grind in January demonstrated. But considering some of the bitter, drawn-out partisan battling that marked some pre-Civil War elections for speaker, McCarthy’s election almost looks smooth by comparison. The U.S. House of Representatives has chosen the winner of a presidential election on two occasions—1800 and 1824. There are several important leadership positions in the House of Representatives. The minority party develops alternatives and agendas of its own and attempts to construct winning coalitions on their behalf. The House of Representatives shares equal responsibility for lawmaking with the U.S.
Congressional Balance of Power: Republican Majority the House Bloomberg Government - Bloomberg Government
Congressional Balance of Power: Republican Majority the House Bloomberg Government.
Posted: Thu, 14 Dec 2023 08:00:00 GMT [source]
The floor leaders and whips of each party are elected by their respective parties in a closed-door caucus by secret ballot.[3] The Speaker-presumptive is assumed to be the incoming Speaker, although not formally selected to be nominated for Speaker by the majority party's caucus. After this period, the Speaker-designate is also chosen in a closed-door session by the largest caucus although the Speaker is formally elevated to the position by a public vote of the entire House when Congress reconvenes. Elections for representatives are held in every even-numbered year, on Election Day the first Tuesday after the first Monday in November. Pursuant to the Uniform Congressional District Act, representatives must be elected from single-member districts. After a census is taken (in a year ending in 0), the year ending in 2 is the first year in which elections for U.S. House districts are based on that census (with the Congress based on those districts starting its term on the following January 3).

No comments:
Post a Comment